Types and characteristics of engine gears
1. Types and characteristics of cylindrical gears
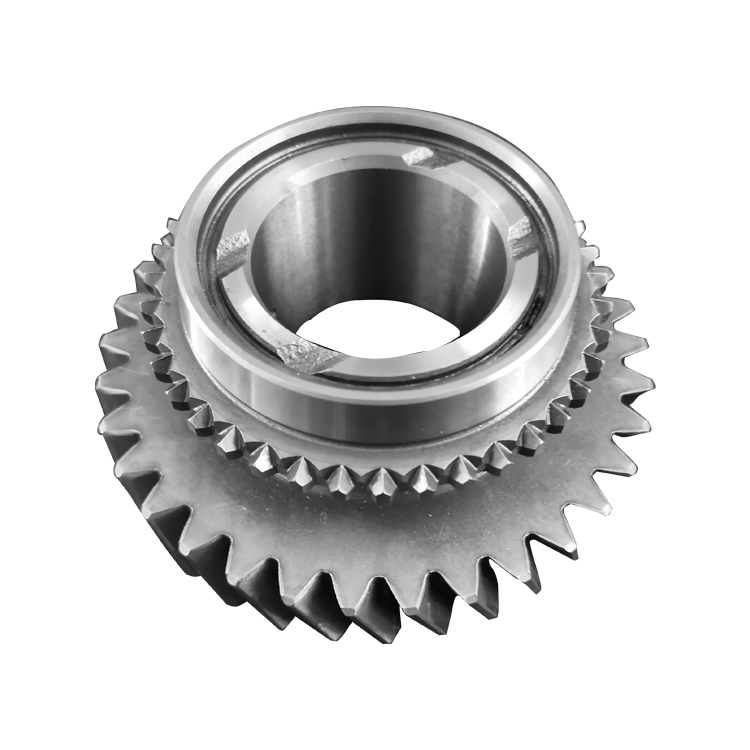
Spur Gears
1) The two shafts of the large and small gears are parallel to each other
2) The long line of the gear tooth is parallel to the gear shaft
3) In external meshing transmission, the two gears rotate in opposite directions; in internal meshing transmission, the two gears rotate in the same direction;
4) The gear can be made into a normal gear with short teeth and can be changed
Helical spur gear
1) The two shafts of the large and small gears are parallel to each other
2) In the case of external meshing transmission, the rotation direction of the two gears is opposite; in the case of internal meshing transmission, the rotation direction of the two gears is the same;
3) The tooth shape can be made into normal teeth, short teeth, and can be changed
4) The gear tooth length direction line and the gear shaft are inclined at an angle
5) The meshing transmission is more stable than the spur gear, and the transmission force is large
6) It is cumbersome to make straighter spur gears
helical gear
1) The two shafts of the large and small gears can be parallel, staggered, and vertical in space
2) The direction of rotation of the large and small gears can be the same or opposite
3) Large and small gears can be equiangular or unequal
4) When the rotation angle of the pinion is large to a certain extent, it becomes a tadpole rod
Gears and Racks
1) The gear meshing with the rack can be a spur gear or a helical gear, which has the characteristics of a spur gear or a helical gear
2) Rack and pinion transmission is to convert rotation into straight line or rotation into rotation
3) The rack is formed when the diameter of the gear is infinite
2. Types and characteristics of bevel gears
Straight bevel gear
1) The two shafts of the large and small gears intersect at the apex of the cone
2) When the cone angle of the large gear section is equal to 90°, it becomes a face gear; if it is greater than 90°, it becomes an internal meshing bevel gear•
Helical bevel gear
1) The tooth line is oblique, tangent to the circle, and the tooth line does not intersect the cone top
2) The rotation angles of the large and small gears are equal and the directions are opposite
3) Straight bevel gear transmission is stable