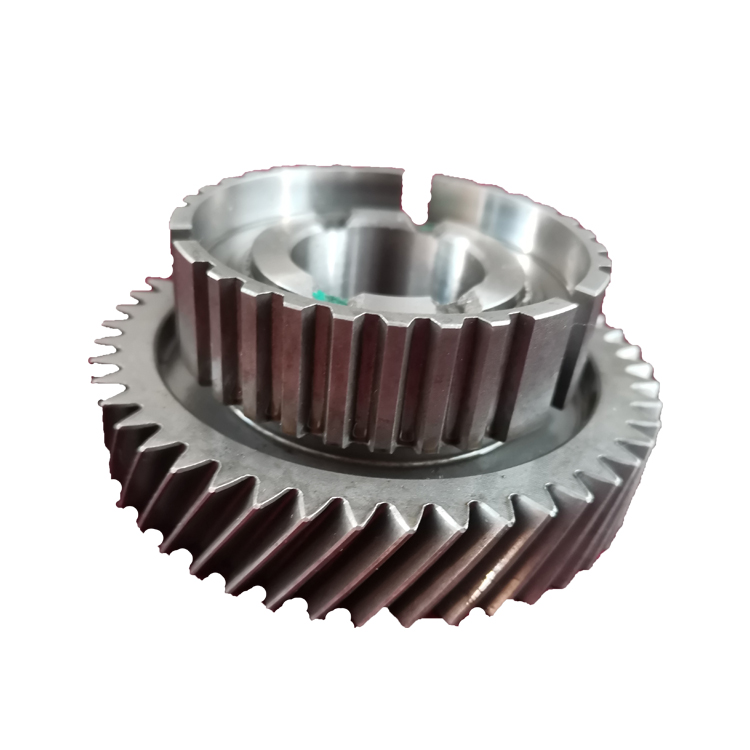
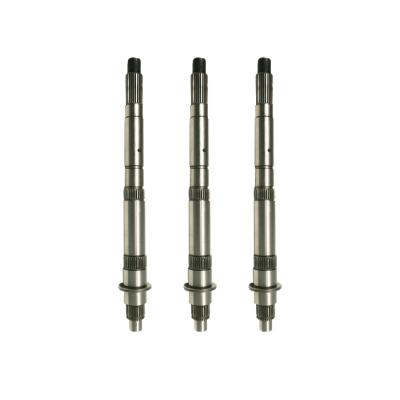
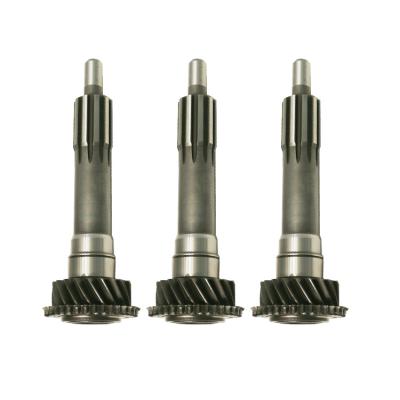
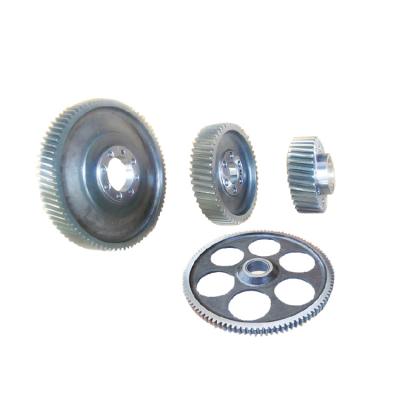
How to check the quality of forgings
The existence of forging defects will affect the processing quality or processing quality of subsequent processes, and some will seriously affect the performance and use of forgings, and even reduce the service life of finished products. Forging quality inspection includes appearance quality inspection and internal quality inspection. Appearance quality inspection mainly refers to the inspection of geometric dimensions, shapes, surface conditions and other items of forgings; internal quality inspection mainly refers to the inspection of chemical composition, macrostructure, microstructure and mechanical properties of forgings.
The appearance quality inspection of forgings is to check the shape of the forgings, whether the geometric dimensions meet the requirements of the drawings, whether there are defects on the surface of the forgings, what are the nature of the defects, and what are their morphological characteristics. The inspection content of the surface condition is generally to check whether there are surface cracks, folds, folds, pits, orange peel, blisters, scars, corrosive pits, bruises, foreign objects, pits, lack of meat, scratches and other defects on the surface of the forging .
Internal quality inspection is to check the internal quality of the forging itself, which is a quality condition that cannot be found by external quality inspection. It includes not only the internal defects of forgings, but also the mechanical properties of forgings. The chemical composition of important components or large forgings should also be analyzed. The mechanical performance and process performance test is to use tensile testing machine, impact testing machine, endurance testing machine, fatigue testing machine, hardness tester and other instruments to determine the mechanical performance and process performance value. Chemical composition tests generally use chemical analysis or spectral analysis to analyze the composition of forgings. The fracture test method is used to check white spots, lamellar and internal cracks (except austenite) of structural steel and stainless steel, check graphite carbon of spring steel forgings and overheating and excessive burning of the above steels. For aluminum, magnesium, copper and other alloys, it is used to check whether the particles are fine and uniform, and whether there are defects such as oxide film and oxide inclusions. Use the low-magnification corrosion method to inspect cracks, folds, shrinkage cavities, pore segregation, white spots, looseness, non-metallic inclusions, and segregation in structural steel, stainless steel, high-temperature alloys, aluminum-aluminum alloys, magnesium-magnesium alloys, copper alloys, titanium alloys, etc. Aggregation, streamline distribution, particle size and distribution, etc. The penetrant testing method can not only inspect magnetic material forgings, but also check surface defects of non-ferromagnetic material forgings, such as cracks, looseness, folding, etc. turn up.